20 Website Speed Optimization Strategies for 2023
In today’s fast-paced digital world, website speed optimization is not just a desirable attribute; it is an essential requirement for successful engagement and business.
High-speed websites offer improved user experience, promoting retention, and simultaneously catering to the ever-decreasing patience of internet users.
Appropriate strategies can be effectively used to achieve optimal website speed, this guide will help you catch up on the state of affairs with some useful tips.
Table of Contents
- What is Page Speed Optimization
- What is an Optimal Website Speed?
- How to Test Speed for your website
- Why do you need Speed Optimization for your website?
What is Page Speed Optimization
The faster your website loads, the better experience users will have, which can lead to better engagement and higher conversion rates.
Optimizing website speed is a complex process involving strategic planning and decision making through a website’s life cycle.
What is an Optimal Website Speed?
The “optimal” speed for a website can depend on several factors, including the type of content on the website and the expectations of its users. However, as a general guideline, it’s commonly recommended that a web page should load within 2-6 seconds.
Why is it important you might think? Well here’s why:
- Bounce rate (%age users who leave without engagement) for a website increases to 32% when load speed changes from 1 to 3 seconds.
- To achieve a bounce rate < 10%, a website should load within 2 sec.
- 79% of shopper are less likely to buy on a website that loads slowly.
- 47% of users expect websites to load under 3 sec
It’s worth noting that these are abstract targets, and meeting them doesn’t guarantee your website will rank highly in Google’s search results. There are many other factors involved in search rankings, but speed is increasingly important.
Also, while improving speed is important, it shouldn’t come at the expense of usability, aesthetics, or functionality. The ultimate goal is to provide a high-quality user experience, and speed is just one aspect of that.
How to Test Speed for your website
Testing website speed effectively involves using a combination of tools and techniques to identify areas where your site’s performance can be improved. Here are some steps you can take to test your website’s speed effectively:
Test Speed During Development: You should ideally keep track of your website’s performance and speed metrics even before it is deployed.
This can easily be done by using the performance and speed testing tools built into the “Developer Tools” section of the browser you use while testing local developments.
For Example,
- Use Online Tools: There are a number of online tools that can provide insights into your site’s speed and overall performance:
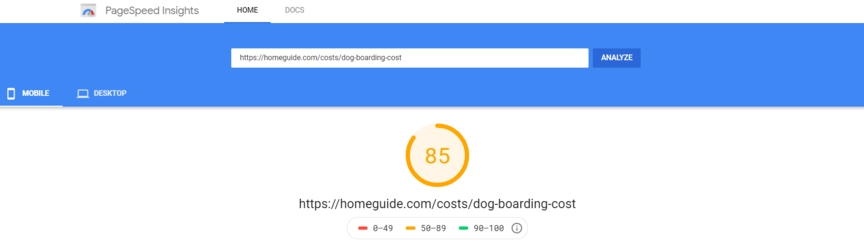
- Google PageSpeed Insights: This is a free tool from Google that analyzes the content of a web page and generates suggestions to make that page faster. It provides separate scores for mobile and desktop performance and offers suggestions for improvement.
- Analyze Key Metrics: When using these tools, there are some key metrics to pay attention to, including:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): This is the time it takes for a user’s browser to receive the first byte of page data from the server. A high TTFB can indicate server issues.
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): This is the time it takes for the first piece of content to appear on screen.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures the time it takes for the largest image or text block to become visible.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures how much the elements on your page shift around during load time. A low CLS score means your site is visually stable.
- Total Blocking Time (TBT) / Time to Interactive (TTI): These measure how long it takes for your page to become fully interactive.
- Test Different Pages: Don’t just test your home page. Test a variety of pages on your site, including product pages, blog posts, and your checkout page.
- Test Mobile Performance: With more than half of web traffic now coming from mobile devices, it’s critical to test how your site performs for these users. Many of the tools mentioned above provide separate scores for mobile and desktop performance.
- Regular Testing: Website speed testing shouldn’t be a one-time task. It should be part of a regular routine. This is especially true if you’re regularly updating or adding to your site.
By using these steps, you can effectively test your website speed and identify areas where performance can be improved.
What Is a Good Website Speed?
Research shows that the amount of time a user will wait before losing focus is roughly from 0.3 to 3 seconds. That means that you should aim to show some content to the user in under 3 seconds. By using Core Web Vitals, then these are the recommended thresholds that you should aim for:
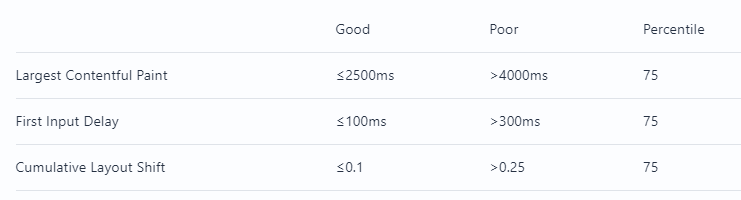
You can read more about what criteria Google used to arrive at these thresholds here.
Note that when measuring page load time it’s best to try to get as much data as possible, from all types of visits. For example, you will need to have data for both desktop and mobile devices. The reality is that you will most likely need to do extra work to get the same performance on mobile devices, even when the metrics for desktop devices are well under the thresholds mentioned above.
Why do you need Speed Optimization for your website?
The importance of testing and optimizing a website’s speed and performance has only increased over the years. As we laid out in numbers on bounce rate and conversion rates in a previous section, it’s clear why tech businesses are focused on it.
Here are some more logical reasons for you to consider improving your website speed and understand the reasons why it is even more critical in 2023:
- User Experience (UX): Slow website speeds can frustrate users, leading to a decrease in user satisfaction and engagement. A smooth, responsive user experience can encourage users to stay on your site longer, interact more with your content, and be more likely to convert (for example, make a purchase, sign up for a newsletter, etc.).
- Mobile Internet Use: The use of mobile devices for internet browsing has grown exponentially. Mobile users often have different connectivity and speed conditions, making speed and performance optimization even more crucial.
- SEO Ranking: Search engines, like Google, consider site speed as a ranking factor. Faster websites are more likely to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs), resulting in more visibility and traffic. Google implemented a new ranking algorithm called Core Web Vitals, which focuses on user experience, including loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Ecommerce Growth: The global pandemic in 2020 and 2021 has resulted in a substantial increase in online shopping and e-commerce activities, a trend that likely continues in 2023. For online retailers, website speed and performance directly impact sales and revenue.
- Increasing Web Complexity: Web applications are becoming increasingly complex with more scripts, images, third-party integrations, and high-resolution content than ever before. Making it critical to prioritize speed and performance optimization to ensure the best user experience.
- 5G and Edge Computing: With the ongoing global roll-out of 5G technology and the rise of edge computing, users’ expectations for website performance are higher than ever. These technologies promise significantly faster load times and lower latency.
- Sustainability: There’s an increasing awareness of the environmental impact of digital technologies. More data means more energy consumed, so an optimized, efficient website could also be a more sustainable choice, reducing its carbon footprint.
- Scalability: As your website grows, you will have more users, more page views, and more content. If your website is already slow, growth will only exacerbate the problem. Optimizing your website’s speed ensures that as you grow and scale, your website can handle the increased traffic and content.
- Competitive Advantage: A faster website can give you a competitive advantage. If your website is faster than your competitors’, you’re more likely to retain and attract users. In the online world, where users can go from one site to another in seconds, speed can be a key differentiator.
- Conversion Rates: Slow websites can have a direct impact on conversion rates. So if your website is an online store or relies on user conversions for revenue, optimizing your website’s speed is crucial.
20 Website Speed Optimization Strategies for 2023
Optimizing a website’s speed and performance requires a multifaceted approach, including the need to take dedicated steps at design, development, and deployment levels.
Here are 20 tips that will guide you to better outcomes in the exercise:
Design-Level Optimization
- 1. Design Mobile-First: Given the prevalence of mobile browsing, design your site with mobile users in mind first. These designs are typically more streamlined, which can improve speed.
- 2. Simplify Your Design: A simple, clean design is often faster. Limit the use of heavy design elements and stick to essentials.
- 3. Use Adaptive assets: Make sure images adapt to the screen size of the user, prefer vector formats like .svg and .webp over .jpeg and .png. etc. Web fonts can slow down your site so use them sparingly and only download the specific styles and characters sets you need.
- 4. Limit the Use of Animations: While animations can add visual interest, they can also slow down your site. Use them sparingly.
Development-Level Optimization
- 5. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Removing unnecessary characters, line breaks, and spaces from these files can help reduce their size and improve loading speeds.
- 6. Use Asynchronous Loading for CSS and JavaScript Files: By default, CSS and JavaScript files are loaded synchronously, which can slow down page speed. Asynchronous loading allows multiple files to load simultaneously.
- 7. Reduce Redirects & API calls: Each redirect triggers an additional HTTP request, slowing down your page load speed. Eliminate unnecessary redirects and API calls like AJAX whenever possible.
- 8. Avoid or Limit the Use of Plugins and Widgets: Every plugin or widget you add requires resources to run. Use them sparingly and only when necessary.
- 9. Leverage Caching: Browser caching stores webpage resource files on a local computer when a user visits a webpage. Leveraging caching can make your site faster for repeat visitors.
- 10. Enable Compression: Use compression techniques like Gzip to reduce the size of your CSS, HTML, and JavaScript files.
- 11. Avoid Render-Blocking assets: Where possible, try to defer linked assets loading or use asynchronous loading to prevent it from blocking the first paint of your webpage.
- 12. Optimize Time to First Byte (TTFB): TTFB measures how long the browser waits before receiving the first byte of data from the server. Improving server response time can optimize your TTFB.
- 13. Use Latest Versions of Everything: If your site is built on WordPress or another CMS that uses PHP, using the latest version can provide a significant speed boost. Similarly for other technologies like NodeJS, React, Webpack, SSL/TLS, HTTP etc. use the latest versions to optimize speed and security.
Deployment-Level Optimization
- 14. Choose the right Hosting Provider: A good hosting provider is crucial for site speed. Shared hosting can be slow due to multiple sites on a single server. Consider using VPS or dedicated hosting.
- 15. Use Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN can distribute the load of delivering content by storing a cached version of your site in multiple geographical locations.
- 16. Implement Load Balancing: If your site has heavy traffic, using more than one server to balance the load can speed up response times.
- 17. Optimize Integrations: Regularly optimizing your database and other critical integrations can help improve your site’s performance, particularly for dynamic websites. This can include tasks like removing unnecessary data/connections and running routine clean-ups.
General Best Practices:
- 18. Prioritize Above-The-Fold Content: Make sure that the content appearing on the screen first (above the fold) loads quickly for a better user experience.
- 19. Remove Unnecessary Metadata: Excess metadata in your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can slow down your site. Remove anything that’s not needed.
- 20. Implement Automated Tests, Audits and Reporting: Using automated tests to regularly check for speed and other vital metrics can save your Website from hiccups in performance, or in worst/best case, prevent a total disaster.
Conclusion
Web page speed optimization is a multi-faceted task, pivotal to the success of any website.
Staying ahead in the online world necessitates an ongoing commitment to optimizing website speed, ensuring a superior user experience, and ultimately, driving higher user engagement and conversions.
As the digital landscape becomes increasingly competitive, optimizing web page speed is not just an optional improvement but an indispensable necessity that directly impacts user experience, SEO rankings, and user engagement.
With the right combination of design, development, and deployment strategies, optimal website speed is indeed achievable.
The faster your website loads, displays content, and responds to user input, the lower your bounce rates and the higher your conversions. Here, incremental improvement is critical — while going from slow to supercharged doesn’t happen overnight, any of our 20 website optimization strategies can help jumpstart your need for speed.