What is On-Page SEO?

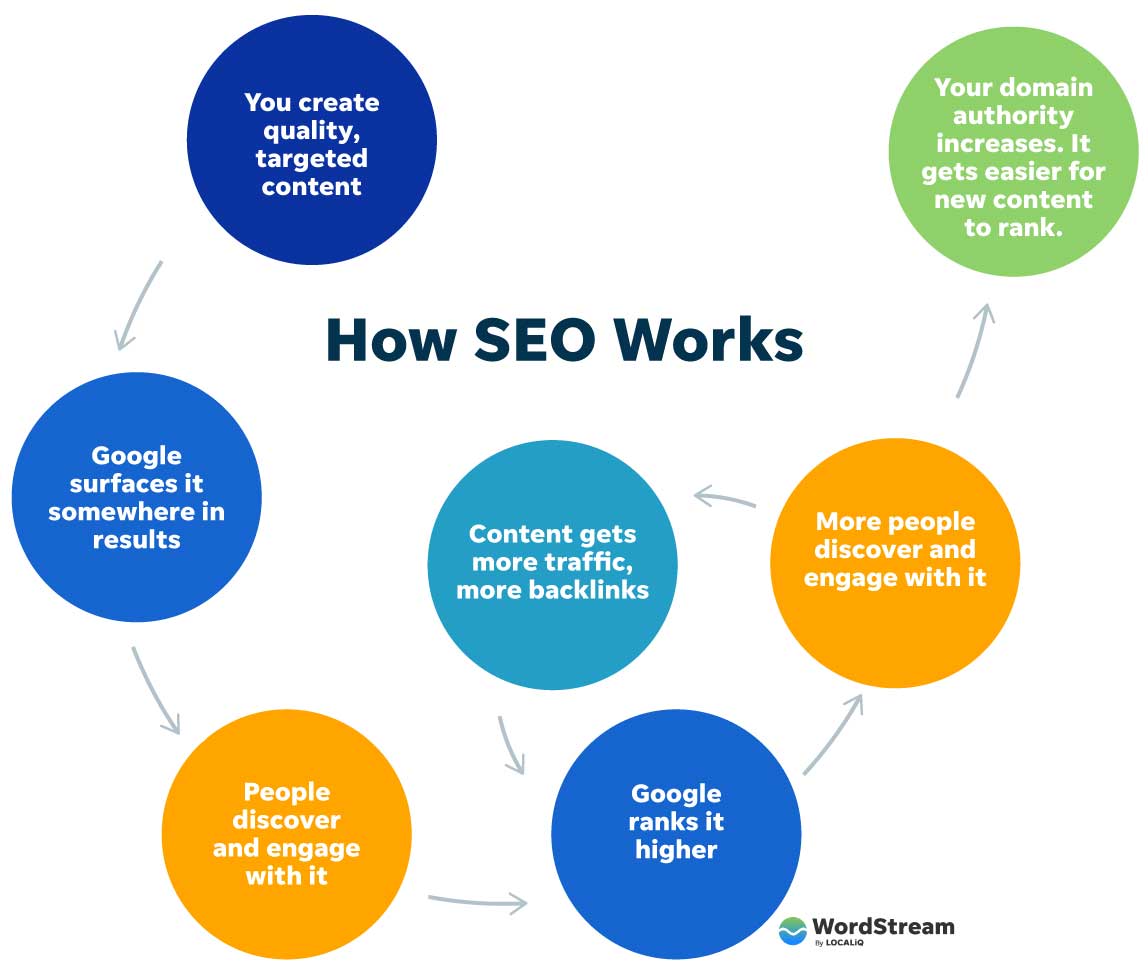
On-page SEO is about building a website that appeals to users with the practice of optimizing elements on your website, like page speed and keyword density, versus factors off your website, like external backlinks, to improve a site’s ranking and visibility in search engines.
Why do On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO leads to higher search rankings, increased traffic to your site, and more conversions. The results of on-page SEO – Search Engine Optimization take time, but once your on-page SEO strategy gets off the ground, it can make your online rankings and sales soar.
On-Page SEO vs. Off-Page SEO: What’s the difference?

On-page SEO differs from off-page SEO, another term you’ll likely encounter when trying to boost your online rankings.
What’s the difference between on-page and off-page SEO?
- On-page SEO: Refers to actions taken on your website, like optimizing your content and streamlining your navigation, to boost your search rankings.
- Off-page SEO: Refers to actions taken off your website, like earning backlinks from other reputable sites, to boost your search rankings.
What on-page SEO ranking factors should I optimize?
With on-page SEO, you have several different on-page ranking factors. You want to optimize all these factors. Taking the time to optimize each of these factors will improve your rankings in search results and make your website more competitive and difficult to beat.
Factors that can impact on-page SEO include:
Core Web Vitals: It’s a set of real-world metrics that quantify a website’s user experience. They measure important dimensions such as visual stability, interactivity and load time. Improving your website’s Core Web Vitals tells Google your site has a positive user experience.

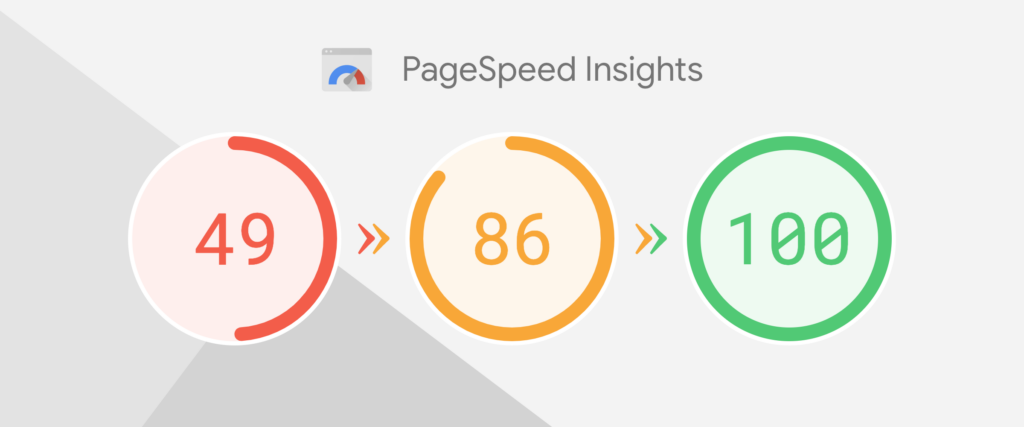
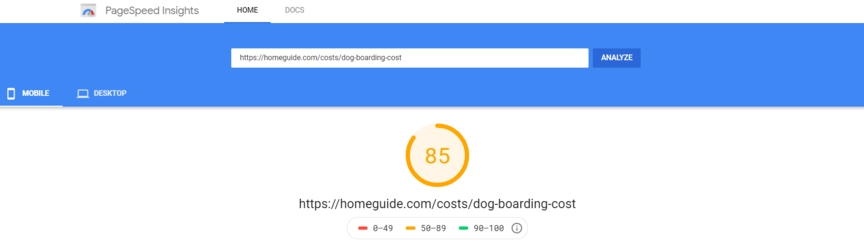
Page speed: Page speed (also known as load time) is an important part of on-page SEO – Google tends to rank faster pages higher than slower ones, and optimizing page speed can also help get more of your pages into Google’s search index. There are lots of ways to improve a page’s speed but images, JavaScript files, caching and compression are good places to start.
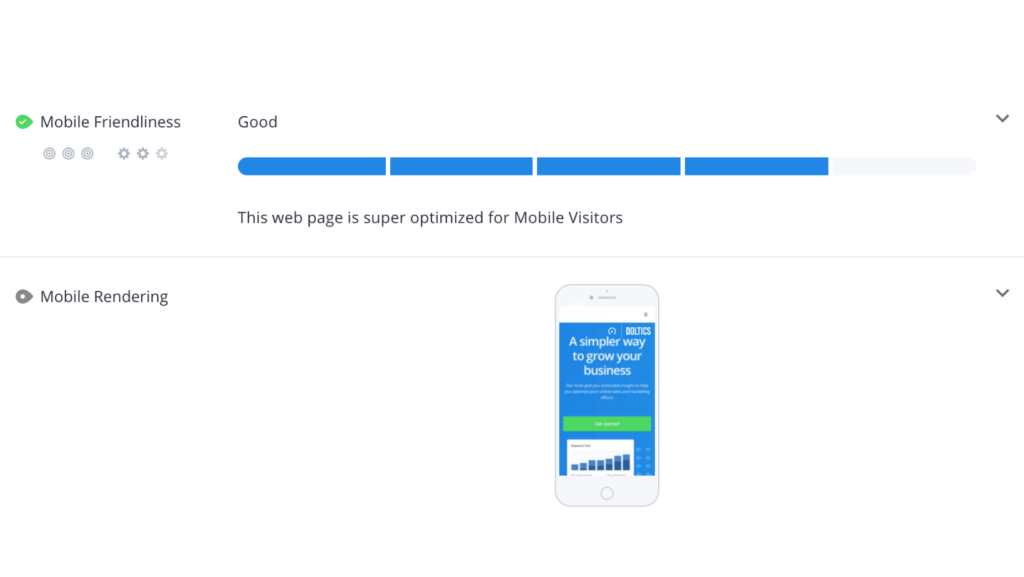
Mobile friendliness: It is a measure of how well a site performs when someone tries to visit and use the site with a mobile device. Mobile friendly pages are able to shrink down to fit on any device’s screen while still allowing people to navigate around the page to achieve their goals. They also prioritize the mobile user experience through responsive design, simple and easy navigation and fast page speeds.
Title tags: Title tags, also called “page titles”, are HTML tags that (as you probably guessed) define the title of the page and describe what the content on the page will be about. For example, the title of this article is “On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO: What’s the Difference?” so the title tag for the page is <title>On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO: What’s the Difference?</title>. When looking for content that’s relevant to a user’s query, Google relies on the keywords in title tags (among other things) to decide whether or not a page is topically related.

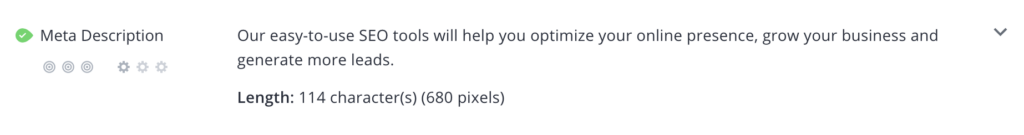
Meta descriptions: Meta descriptions are, like title tags, HTML tags that help describe what the page is about. While Google does use descriptions when deciding if a page is relevant to a query, their main SEO function is to encourage people to click through to your site from search results.
Content quality: When it comes to on-page SEO, content is king. Search engines have a lot of different ways to evaluate content quality, but it really comes down to answering A) Is it useful for the user? B) Is it easy to read? C) Is it unique? and D)Is it relevant to a user’s query? If you can honestly answer “yes” to each of those four questions, your content is in a good place.
HTML headers: HTML headers are HTML tags that specify headlines and subheads within a webpage’s content. They help your website’s visitors better read and understand your content. For on-page SEO, these tags help search engines better understand what the content on a page is about and how it relates to a person’s search query.

Image alt text: Image “alt text” refers to an attribute within an image’s HTML tag that contains a text description of the image. Alt text is used by assistive technologies such as screen readers as well as browsers as a backup when an image fails to load on a page. Search engines look at alt text as a way to decide how relevant an image is to someone’s query. As such, alt text is a very important on-page SEO factor for image searches as well as traditional web search.
Internal linking: Linking to other pages on your site from within your own content is useful as it helps visitors find related content with extra background or context. We do it several times in this article, linking to more in-depth guides to explain important details regarding on and off-page SEO. Internal linking also improves your site’s SEO by helping search engines find new content. Plus, the anchor text you use for your internal links tells search engines what they should expect from the destination page and how it relates to the linking content.
Navigation: In the context of on-page SEO, “navigation” is about making sure all users can access and consume the content on a web page. We’re not talking about how your pages are grouped or linked together (that’s called “site structure”). Google cares a lot about what sort of page it’s recommending to searchers and they want anything they recommend to be accessible to everyone, regardless of disability or browser.

How to evaluate your on-page optimization
Now that you know about on-page SEO, you can evaluate your site’s performance. You can either use a tool to audit your site or you can look at separate pages manually, depending on your preference. If you choose to look manually, you can use these criteria as a basis for on-page optimization.
- Are you using keywords for every page? Have these keywords been delivering visitors? If they haven’t been, why are you still using the keywords?
- Are you linking pages on your site to each other? Could this be a way to help visitors get from one point to another with only a click or two?
- Does your site load quickly? Or do some pages take a long time to load? If you’re having problems, find out where the issue lies. A slow-loading website is something neither human nor bot visitors enjoy!
- Does your site have fresh content? Has it been more than one or two years? Has anything changed or is it all still relevant?
“Remember: SEO is not a one-and-done deal. It’s something you should continually improve upon. You should treat this On-Page SEO Template as a living, breathing document that will help guide your SEO strategy for months (or years) to come.”
Pro tip: Read our Off- Page SEO Optimization to know how it covers anything you can optimize outside of your site (or externally) in an attempt to boost your rankings.